Placenta Accreta Part I - Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Imaging
/Today we welcome two special guests to the podcast — Dr. Scott Shainker, who is an assistant professor at Beth Israel Deaconess in Boston, MA, and Dr. Brett Einerson, who is an assistant professor at the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, UT. Both Dr. Shainker and Dr. Einerson are experts in the world of placenta accreta spectrum, with numerous publications, guideline papers, and advocacy efforts to their names. We did a two part series with them on PAS. This first episode, we focus on pathology, diagnosis, and imaging. Next week, we’ll get into management and future directions.
For further reading, check out ACOG’s Obstetric Care Consensus on PAS.
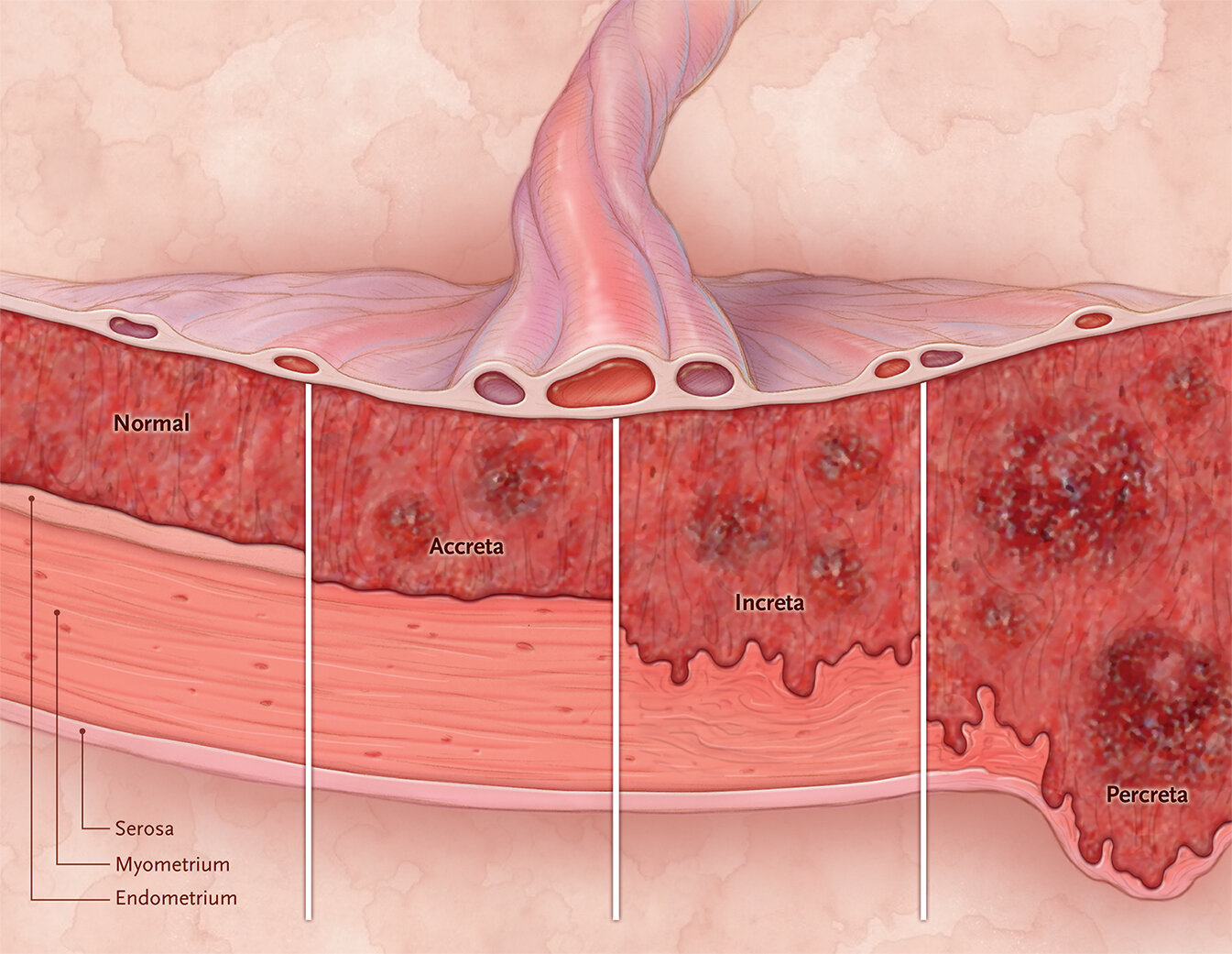
PAS has traditionally been thought of as an “invasive” disease, but that thinking is evolving to think of PAS as a disease of uterine dehiscence. The loss of the uterine decidua due to prior uterine scarring (i.e., due to surgery) brings about abnormal attachment and a “superhighway of vascularity,” thus that when delivery comes, the placenta fails to separate normally. Uterine muscle dehiscence likely accounts for the degree of invasiveness. It’s likely that cesarean scar pregnancies are a precursor to PAS.
https://resident360.nejm.org/clinical-pearls/placenta-accreta-spectrum
The PAS diagnosis and terminology is also changing, from the traditional accreta / increta / percreta divide seen above, to a FIGO staging system with both surgical and pathologic criteria. You can review those here.
We review some of the risk factors, but far and away the biggest is a combination of a prior cesarean and placenta previa. Dr. Shainker mentions Dr. Robert Silver’s landmark paper on this - the percentages are worth committing to memory. Other risk factors include other types of uterine surgery like abdominal myomectomy; IVF and ART; and potentially dilation and curettage, though that is controversial.
Imaging is great in research capacities with high sensitivity (approaching 90+%), but only 50% of patients with accreta know about it before delivery. So the real world sensitivity is very poor. Risk factors should raise suspicion primarily, and the use of imaging help guide your preoperative suspicion. SMFM has now published a consensus on ultrasound diagnosis, which is the gold standard. More data should hopefully improve the real-world detection rates for PAS.